 There is a distinct shift in how organisations are now viewing cybersecurity, with forward-thinking organisations understanding that an investment in cybersecurity and privacy solutions can facilitate business growth and foster innovation.
There is a distinct shift in how organisations are now viewing cybersecurity, with forward-thinking organisations understanding that an investment in cybersecurity and privacy solutions can facilitate business growth and foster innovation.
The Global State of Information Security® Survey 2017, released in October 2016 by PwC in conjunction with CIO and CSO magazines, examines how executives are adopting technology and collaborative approaches to cybersecurity and privacy to manage threats and achieve competitive advantages. Samuel Sinn, Cybersecurity and Privacy Partner, PwC China, provides some highlights from the report below.
Many organisations no longer view cybersecurity as a barrier to change or as an IT cost. According to the Global State of Information Security® Survey 2017, 59 per cent of respondents said they have increased cybersecurity spending as a result of the digitisation of their business ecosystem. In this process, organisations not only create products, but also deliver complementary software-based services for products that extend opportunities for customer engagement and growth.
There is a distinct transformation in how business leaders are viewing cybersecurity and technology – no longer seeing technology as a threat and understanding that cybersecurity is a vital component that must be adopted into the business framework. To remain competitive, organisations today must make a budgetary commitment to the integration of cybersecurity with digitisation from the outset.
Survey results also found that as trust in cloud models deepens, organisations are running more sensitive business functions on the cloud. Today, the majority of organisations around the world—63 per cent of survey respondents—say they run IT services in the cloud. Additionally, approximately one-third of organisations surveyed were found to entrust finance and operations to cloud providers, reflecting the extent to which trust in cloud models is growing.
The fusion of advanced technologies with cloud architectures can empower organisations to quickly identify and respond to threats, better understand customers and the business ecosystem, and ultimately reduce costs. Cloud models have become more popular in recent years, and that trend will likely only continue as the benefits become increasingly clear.
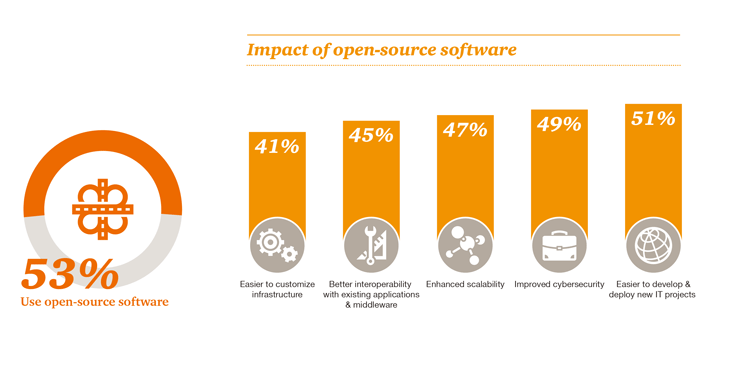
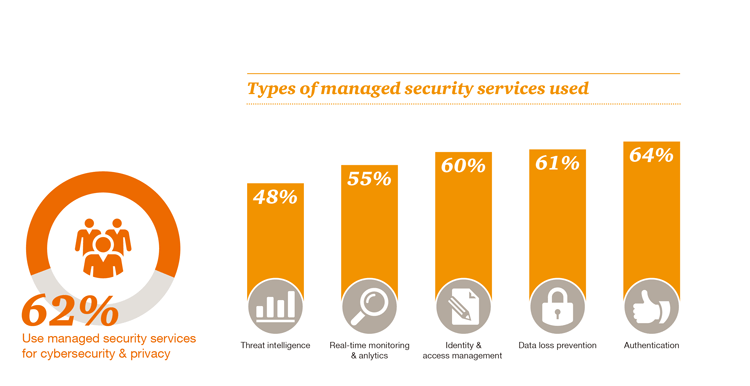
According to survey respondents, organisations are also embracing both managed security services and open-source software to enhance cybersecurity capabilities, signalling that businesses are making cybersecurity a priority despite many not having the necessary in-house capabilities and lacking the talent required to fill key positions. More than half (53 per cent) of respondents employ open-source software and 62 per cent of respondents say they use managed security services for cybersecurity and privacy – relying on managed security services for highly technical initiatives such as authentication, data loss prevention and identity management.
Designing and implementing a cybersecurity and privacy programme is challenging enough, but once a programme is in place components must be thoroughly integrated, professionally managed and continuously improved. As this can be difficult for resource-constrained organisations, many are adopting managed security services and utilising open-source software.
The survey responses in Mainland China and Hong Kong also indicate severe cybersecurity challenges. The average number of detected security incidents by survey respondents in Mainland China and Hong Kong reached 2,577 in 2016, marking a 969 per cent increase from 2014, and more than double the average recorded for 2015. The increasing domestic trend contrasts with global survey data which points to a slight decline, with a total worldwide average of 4,782 detected incidents reported in 2016, reflecting a three per cent drop from the global average number of detected incidents reported since 2014.
In terms of investment, survey responses indicate a decrease was seen in information security budgets by companies from Mainland China and Hong Kong in 2016, with a 7.6 per cent reduction compared to the previous year. Nevertheless, 88 per cent of those respondents acknowledged that digitisation has impacted their information security spending in 2016, and highlighted cybersecurity alignment with business strategy and security governance as the top priority for such spending over the period. Additionally, 31.5 per cent of respondents from Mainland China and Hong Kong registered a specific intention to invest in advanced security technologies including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies.
We can see forward looking organisations in the domestic market are investing in advanced cybersecurity to define and defend their own differentiated value, while safeguarding paths to robust business growth.
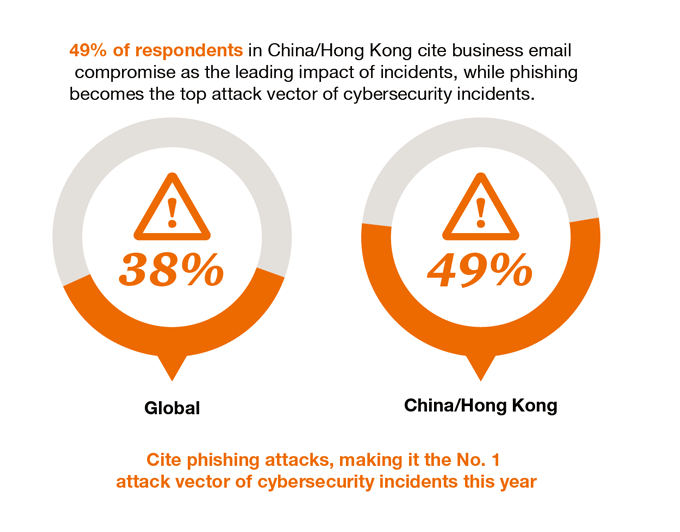
With regard to the nature of security incidents, 49 per cent of respondents from Mainland China and Hong Kong cited phishing as the top vector for cybersecurity issues over the last year, while business email formed the biggest impact of incidents for the period. Once again, the role of insiders was flagged as the most common source of detected incidents. Business insiders accounted for 44 per cent of all detected security incidents that were reported by respondents in Mainland China and Hong Kong this year. The figure reflects an increase from the 40 per cent attributed to insiders in the prior year, and stands above the global average of 41 per cent of incidents attributed to insiders in 2016. Also of note, 34 per cent of domestic respondents experienced security incidents attributed to competitors, markedly higher than the global average of 23 per cent.
As organisations face evolving opportunities and threats, steps to strengthen cybersecurity with Internet-of-Things-connected devices have become mainstream, along with the allocation of sensitive business functions to the cloud. Data for 2016 shows 57 per cent of survey respondents in Mainland China and Hong Kong are investing in a security strategy for the Internet of Things and 45 per cent of all IT services now run via cloud service providers, which compare to 46 per cent and 48 per cent with global respondents respectively.
Concurrently, both managed security services and open-source software are increasingly used to enhance capabilities, including cybersecurity, with some 75 per cent of respondents from Mainland China and Hong Kong documenting that they employ open-source software, compared to 53 per cent of respondents globally.
We are seeing more companies taking steps to develop their IT security systems in response to the real and rising threat of cyber risks. Adaptation of cloud technologies and open-source software signal how businesses are making cybersecurity a priority, despite not necessarily having the in-house capabilities in place just yet. While encouraging, companies will need to ensure their technology can keep up with these growing cybersecurity threats.
At PwC, our purpose is to build trust in society and solve important problems. We’re a network of firms in 157 countries with more than 208,000 people who are committed to delivering quality in assurance, advisory and tax services.
Samuel Sinn has more than 25 years of experience in providing information security, IT risk management and IT audit services to state-owned enterprises, listed companies and multinational corporations in China, Hong Kong and the United States. He has extensive experience in advising on technology risk management within the financial services industry, as well as exposures to industries, including telecommunication, technology and manufacturing.
 The Global State of Information Security® Survey 2017 (GSISS 2017) was launched in China in November 2016, with China observations. GSISS 2017 is a worldwide study by PwC, CIO and CSO Magazine, which was conducted online from April 2016 to June 2016. GSISS 2017 is conducted among readers of CSO and CIO Magazine and clients of PwC from 133 countries, with responses from more than 10,000 CEOs, CFOs, CIOs, CISOs, CSOs, VPs and directors of IT and security practices worldwide. Forty-eight per cent of respondents from organisations with revenue of USD500 million+, while more than 40 questions on topics related to privacy and information security and how businesses are implementing innovative new safeguards. Locally we have got 440+ respondents from China/Hong Kong.
The Global State of Information Security® Survey 2017 (GSISS 2017) was launched in China in November 2016, with China observations. GSISS 2017 is a worldwide study by PwC, CIO and CSO Magazine, which was conducted online from April 2016 to June 2016. GSISS 2017 is conducted among readers of CSO and CIO Magazine and clients of PwC from 133 countries, with responses from more than 10,000 CEOs, CFOs, CIOs, CISOs, CSOs, VPs and directors of IT and security practices worldwide. Forty-eight per cent of respondents from organisations with revenue of USD500 million+, while more than 40 questions on topics related to privacy and information security and how businesses are implementing innovative new safeguards. Locally we have got 440+ respondents from China/Hong Kong.




Recent Comments